The current position:Home > Information dynamic
> Industry Trends
How to reduce cross infection with disposable anti reflux drainage bags
source:www.cnboyi.net | Release time:2025年11月10日1. Core protection mechanism
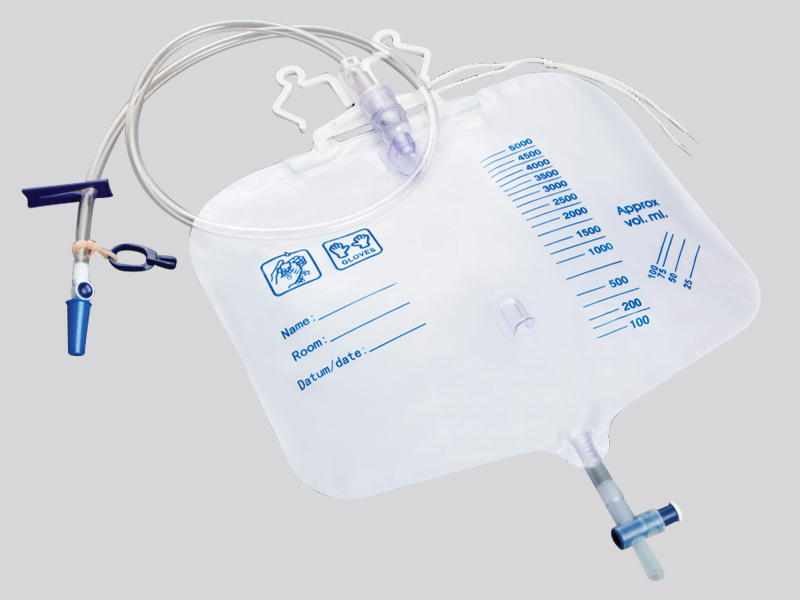
Anti backflow structure design, with a one-way valve or anti backflow membrane inside the bag, allowing only drainage fluid to flow into the bag from the catheter, preventing the fluid from flowing back into the patient's body or catheter in the opposite direction, and avoiding retrograde infection of pathogens in the drainage fluid.
Disposable feature, each patient uses a separate set, and after use, it is disposed of according to medical waste standards, without reuse, to prevent cross contamination between different patients.
Sealed connection and material, with sealed design at the catheter, drainage bag, and joint to reduce the risk of leakage; The bag body is made of medical grade sterile material, and the production process has undergone sterilization treatment, with no pathogen contamination before use.
2. Auxiliary protection details
Clear capacity scale and exhaust port make it easy to observe the drainage fluid situation. The exhaust port design can avoid splashing of drainage fluid when pouring, reducing the risk of infection for medical staff.
Some products are equipped with connectors to reduce the risk of needle stick injuries for medical staff during operation, indirectly reducing blood borne infections.
Suitable for various drainage scenarios, it can be correctly docked with catheters, drainage tubes, etc., reducing the invasion of pathogens caused by connection gaps.
Prev:
What should be noted when using disposable precis…
Next:
How to ensure the safety of nutrition infusion th…

 Cn
Cn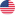 En
En WeChat ID:
WeChat ID:





 Contact us
Contact us
 Add WeChat
Add WeChat
 Telephone
Telephone